Taking Care of Your Prostate: A Man's Guide to Prostate Health
Introduction
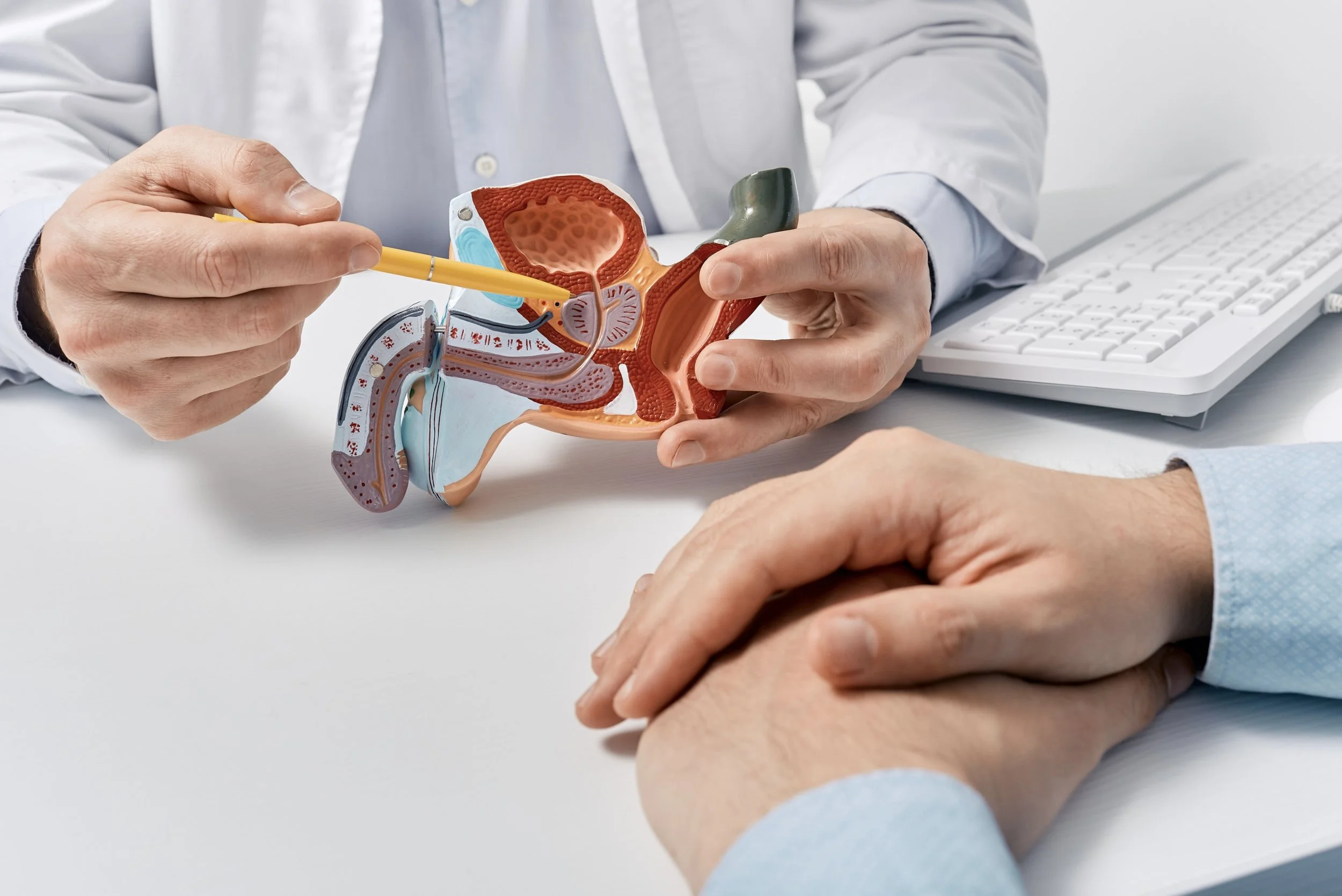
Your prostate gland, a walnut-sized organ located below the bladder, plays a crucial role in male reproductive health. Despite its small size, it can have a significant impact on your overall well-being. Understanding its function, potential issues, and preventive measures is essential for men of all ages.
What is the Prostate Gland?
The prostate gland is part of the male reproductive system. It produces a fluid that nourishes and transports sperm. As men age, the prostate gland often enlarges, which can lead to various urinary symptoms.
Why is Prostate Health Important?
Maintaining prostate health is vital for several reasons:
Quality of Life: Prostate issues can significantly impact your quality of life, affecting your sleep, energy levels, and social activities.
Sexual Health: Prostate problems can interfere with sexual function, leading to erectile dysfunction and decreased libido.
Serious Health Risks: In some cases, prostate issues can lead to more serious conditions, such as prostate cancer.
Common Prostate Problems
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH):
This condition, often referred to as an enlarged prostate, commonly affects men over the age of 50.
Symptoms include frequent urination, difficulty starting or stopping urination, weak urine flow, and nighttime awakenings to urinate.
Treatment options for BPH include medication, minimally invasive procedures, and surgery.
Prostate Cancer:
Prostate cancer is one of the most common cancers in men, particularly those over the age of 50.
Early detection through regular screenings, such as the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) test and digital rectal exam (DRE), is crucial for successful treatment.
Treatment options for prostate cancer vary depending on the stage and severity of the disease and may include surgery, radiation therapy, hormone therapy, and chemotherapy.
Prostatitis:
Prostatitis is inflammation of the prostate gland, which can affect men of all ages, but is most common in men aged 30-50.
Symptoms include pain in the pelvic area, difficulty urinating, frequent urination, and pain during ejaculation.
Treatment typically involves antibiotics to combat bacterial infections, along with pain relievers and other medications.
Chronic Prostatitis/Chronic Pelvic Pain Syndrome (CPPS):
Chronic prostatitis/chronic pelvic pain syndrome (CPPS) is a long-term condition that causes chronic pain in the pelvic area. It can affect men of all ages, but is most common in men aged 20-50.
Symptoms can include pain in the testicles, perineum, lower back, or abdomen.
Treatment for CPPS may involve medication, physical therapy, and lifestyle changes.
The Role of a Physiotherapist in Prostate Health
While a physiotherapist is not a medical doctor, they can play a significant role in managing prostate-related issues. Pelvic floor physiotherapy can help:
Improve urinary symptoms: By strengthening the pelvic floor muscles, physiotherapy can help alleviate urinary frequency, urgency, and incontinence.
Enhance sexual function: Pelvic floor exercises can improve erectile function and sexual satisfaction.
Reduce pain: Physiotherapy techniques can help alleviate pain associated with prostate conditions.
Promote relaxation and stress management: Stress can exacerbate prostate problems. Relaxation techniques, such as deep breathing and meditation, can help reduce stress and improve overall well-being.
Preventive Measures for Prostate Health
To maintain optimal prostate health, consider the following tips:
Regular Check-ups: Schedule regular check-ups with your doctor, especially after the age of 50, to monitor your prostate health.
Healthy Diet: A diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can help reduce the risk of prostate problems. Limit red meat and processed foods.
Regular Exercise: Physical activity can help improve overall health, including prostate health. Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.
Hydration: Drinking plenty of water can help prevent urinary tract infections and other prostate issues.
Weight Management: Maintaining a healthy weight can reduce the risk of prostate problems.
Regular Ejaculation: Regular ejaculation, through sexual activity or masturbation, can help reduce the risk of prostate inflammation and infection.
Stress Management: Practice stress-reducing techniques, such as yoga, meditation, or deep breathing.
By understanding the importance of prostate health and taking proactive steps to protect your prostate, you can improve your quality of life and reduce your risk of serious health problems.